
Ignou Question Bank (473)
Ignou Question Bank from previous year papers
Children categories

Ms-422 Question Bank (6)
IGNOU MBA BOOKS IGNOU MBA ASSIGNMENTS New
Ms-422 Question Bank, Bank financial Management

Ms-495, Question Bank (2)
IGNOU MBA BOOKS IGNOU MBA ASSIGNMENTS New
Ms-495, Question Bank, Ethics And Corporate Governance In Banks

IB0-04 Question Bank (3)
IB0-04 Quesiton Bank, Export - Import Procedures And Documentation

MC0-03 Question Bank (2)
MC0-03 Question Bank, Research Methodology And Statistical Analysis
MS-1 SOLVED PAPER 2018 Featured
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.com
MS-001
December, 2017
MS-001 : MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS AND
BEHAVIOUR
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) There are two Sections : A and B.
(ii) Attempt any three questions from Section-A,
each question carries 20 marks.
(ill) Section-B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
1. Explain the need for MBO in an organization and the process involved in it. Briefly discuss the benefits of having MBO in an organization.
2. Briefly describe the antecedents of organizational change and the strategies to cope with the change.
3. Briefly discuss the factors influencing the choice of organizational structure. Describe any two types of structures and their advantages and disadvantages.
4. Discuss the determinants of interpersonal behaviour. Briefly explain how to develop
interpersonal skills.
5.
Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Barriers to effective communication
(b) Gamesman model of decision-making
(c) Group cohesiveness
(d) Methods of control
(e) Prerequisites for effective delegation
SECTION - B
6.
Read the following case carefully and answer the questions given at the end :
Modern Bank Limited was established in 1938 by Vasudev Mudaliar as a private bank. The bank grew to become a 100 crore business by 1944 and a 500 crore business by 1960. Vasudev Mudaliar was succeeded in the business by his sons. In 1974, an investor, Sudhakar Gupta, bought 51% equity in the bank and assumed charge as chairman. The bank gradually expanded in the four southern states and grew to be a business worth
3,200 crore by 1985. In 1987, Sudhakar Gupta brought in Arvind Jain, a young MBA graduate, as the MD of the bank. Arvind Jain focused his energies on building the brand of the bank among the traditional segments and simultaneously focused on building brand equity among the middle class. During this period the bank recorded continuous business growth and by 1997, the bank's total business stood at 12,000 crore.
Arvind Jain was a fiery young man who essentially believed in turnaround performance.
His style of leadership was autocratic and he believed that people around him should be
committed to executing his orders rather than wasting time on debates and discussions. He formed a core group of top executives to strategize and monitor the implementation of action plans. Being a traditional bank where hierarchy and authority were respected, it was not long before everyone adjusted to the new style of functioning. Everybody from the branch offices, regional offices, and the head office, religiously followed the orders of the top management. The result was a stupendous success. The bank became a force to reckon with among the private sector banks in southern
• recruiting top-notch professionals
re-engineering the corporate brand of the bank
emphasizing marketing and business development
• a top-down approach in the decisionmaking process
• adoption of technology for modernizing business operations.
Along with the positive developments were a few negative aspects :
• centralization of the bank's functioning
• formation of a coterie which wielded power in the bank
• emphasis on performance at any cost rather than on means
• frustration and disillusionment of the employees at large
Parallel with these developments, there were other developments too in the bank. Differences arose between the promoter Sudhakar Gupta and the MD Arvind Jain, which eventually led to the resignation and exit of the latter from the bank.
A few of his faithful followers too exited from the bank. The chairman, in consultation with the board, appointed a senior banking professional, Manoj Pillai, from an established public sector bank, as the MD of Modern Bank. On assuming charge, Manoj Pillai reshuffled the top management and set up a new team at the corporate office. It was his belief that systems and procedures should take precedence over individuals in the bank, and that after goals are set, executive should be given freedom to
perform. A few hallmarks of his leadership and management approach in the bank were as follows
• emphasis on streamlining systems and procedures
• nurturing employees to strictly adhere to laid-down norms/systems.
• training of existing employees in core areas such as credit, audit, etc.
recruitment of young professionals, i.e.,
MBA, M.Com., etc. as management trainees and their induction into the bank to bring
in fresh blood and enthusiasm.
• strengthening the training system for under-taking training and induction
responsibilities.
• posting of successful line personnel as faculty in Staff Training Colleges to drive
home the importance of training to the employees of the bank.
• continuing the technology upgradation
processes undertaken during earlier review.
However, the employees of the bank, especially the top and middle management, who
were used to following the instructions of the central command and carrying out the decisions of centralized decision making could not adjust to the new leadership approach. The top executives started perceiving the new leader as weak, due to lack of the charisma and strong drive that they had seen in the earlier leader. Further,
the emphasis on re-engineering the systems led to stagnation of product innovation and during
the three years Manoj Pillai was with the bank, no product could be launched.
The bank slowly lost its market share and recorded a negative growth during the period
1997-2000. There was an interesting development in 1999, when the promoter offloaded a minus stake to a multinational bank. The changed business interest of the promoter led to further offloading of stake in favour of the multinational bank. As a result the majority stake in the bank stood transferred to the multinational bank.
The new management undertook a series of measures to re-engineer and redefine the brand and image of the bank. Some of the salient features of these measures were :
• upgrading the technology of the bank
• gearing up the bank for various technology initiatives such as core banking solutions,
Internet banking, call centre and help desk, etc.
• recruitment of a new breed of professionals at all levels and in all functional areas to
cater to the needs of the bank.
• strict implementation of the performance planning and measurement approaches.
• implementation of Cost To Company (CTC) approach for all the middle and top
management officials of the bank.
• voluntary retirement scheme (VRS) for employees found to be lacking in the new
set of competence.
• massive exercise of re-branding and re-engineering the product portfolio of the
bank.
• creation of a core team of young professionals to continuously work on
re-branding and product re-engineering.
• improving the learning infrastructure by networking the IT infrastructure with the
existing training infrastructure to leverage the advantages.
During the initial transformation period, the old genre of employees were frustrated by the higher compensation given to the new recruits as well as the importance accorded to them as against the existing employees. This led to the exodus of a large number of employees through the voluntary retirement scheme. The remaining
employees were in a state of confusion about the direction the bank was heading in.
In the meantime, the new management recruited an MD, Vikrant Advani, a senior
banking professional with over 20 years of experience, to lead the bank, along with a new
set of initiatives. After assuming charge, Vikrant Advani made it a point to personally interact with all senior executives. He communicated with all employees about the transformation process and the steps undertaken by the bank for the purpose.
As a step towards implementing the knowledge management process in the bank, the
training department launched a whole set of initiatives with the help of the IT department as given below :
• setting-up of corporate Intranet for the bank with built-in features such as bulletin
boards, discussion and chat rooms, etc.
• integrating the e-learning software with the Intranet to provide learning inputs to
employees.
• identifying resource persons area-wise and making them available online to disseminate
learning across the organization.
• collecting the critical experience of employees in various functional areas and
presenting them as case studies for employees to learn.
• providing all the information and circulars
related to various systems and procedures of the bank online to empower the
employees with information.
• tying up with learning content providers for continuously updating the learning content.
Questions :
(a) Analyse the case from the learning inputs from organizational perspective.
(b) Examine whether the technology transformation processes will lead to a
change in organizational culture.
(c) Do you feel that the bank is on the right track ? Why ?
(d) Suggest steps for improving the knowledge management processes in the bank.
MS-001 : MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS AND
BEHAVIOUR
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) There are two Sections - A and B.
(ii) Attempt any three questions from Section-A,
each question carries 20 marks.
(iii) Section-B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
1. Briefly describe different responsibilities of a manager and their relevance citing examples.
2. What is meant by mission, objectives, strategy and policies ? Discuss the relevance of these from organizational context.
3. Discuss and describe different dimensions and determinants of organisational culture.
4. Discuss formal and informal organisation structures and the importance of decentralization in an organization.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Formulating a plan
(b) Johari Window
(c) Types of power
(d) Conflict-defusion strategies
(e) Brain storming
SECTION - B
6. Read the case carefully and answer the questions
given at the end.
Mr Sondhi,
He himself had a mind to apply some of the Japanese Techniques in his company, India Gears. During his visit to Japan, Mr Sondhi was deeply impressed by several techniques used by the Japanese such as Just in Time, Poka Yoke, Kaizen, Quality circles, Total Employee involvement, etc. He specifically noted that a Japanese employee worked for his Nation rather than just
trying to make more money. He ascribed this to homogeneous culture, religion and language which tied tim Japanese in a close emotional bond. One aspect of the Japanese way of doing business which impressed Mr. Sondhi was the way the Japanese companies did outsourcing of several components to outside small companies. According to Sondhi, this permitted the Japanese firms to focus on their core competent areas in a
better manner. In addition the vendors were able to supply the needed materials and components, just-in-time thereby reducing the inventory to manageable levels. Further the size of the plant was reduced which reduced the taxes and effort of managing the in house. Operations became simpler and more effective. One fact observed by
Mr. Sondhi was that the vendors were close relatives of the employees which further increased the ties between the company and its employees. On his return to
were young and enterprising engineering and management graduates searching jobs in and around
Mr. Sen proposed that these young graduates could be helped by India Gears to start
their own ancillary units which could become vendors to their company. The attitude of Mr. Sen was to encourage young talent to start their own ventures. According to Mr. Sen, a part of the initial investment would be done by any manager whose son or daughter started the ancillary. The India Gears would be contributing some percentage of the initial investment. Both Mr. Sen and Mr. Sondhi called a meeting of their trusted Managers. Mr. Mittal from Marketing and supply chain, Mr. Desai from Industrial engineering. Mr. Jain from maintenance. Mr. Nagpal from production and
Mr. Apte from Design and quality. The topic of starting ancillaries was placed on the table, and in the end all the managers unanimously applauded the vision of their bosses. They said in chorus that they would give a thought to this highly magnanimous and collaborative proposal. Soon the ancillaries were started with pomp and show and was hailed as a milestone in the history of India Gears. The managers whose young ones were unit heads were in high spirits. They often used to sing in the praise of Mr. Sen
and Mr. Sondhi about their creative thinking when they used to meet in the afternoons for their executive lunch. They often discussed about the success story of their children with
great enthusiasm. Mr. Sondhi also expected an increase in the organizational effectiveness of India Gears. Looking at the cheerful faces of his managers
Sondhi thought that the managers were highly motivated with the success of the ancillaries run by their sons and daughters and that this would be helpful to India Gears as well. About one year after the starting of the ancillaries the routine Annual audit of India Gears was done by their trusted Chartered Accountant, Mr. Agrawal, a
brilliant pass out of NITIE,
objective ways of presenting the Annual Reports. The audit report gave a shock to Mr. Sen and Mr. Sondhi. The report said that the productivity had declined by 20% and the ROI declined from 20% to 12%. The auditor passed strictures saying that
on a number of occasions certain orders were cancelled due to delay in the delivery to the
customer. There were instances of return of consignment from US and
not meeting International Quality Standards QS9000 laid down by three automobile giants of US, namely, Ford, GM and Chrysler. This had never happened in the past. Seeing this sudden decline in the effectiveness in the Performance of
India Gears, Mr. Sen was in a disturbed mood. He appointed an external Management and Technical Consultant to investigate into the matter.
The consultant demanded certain documents of the company including the personal
records of the managers of the previous year and the current year to investigate into why things had gone wrong. After a detailed study of the records and interview of junior and senior personnel he discovered certain startling facts. He summarized the important points and placed them before Mr. Sondhi and Mr. Sen as under. 1. The absenteeism level of some managers had increased a great deal. These were the managers whose children had started the ancillary. Among the problems discovered
were refusal of Design to change the customer's drawings from DIN standard to
ISO standard, reduced use of the imported Carl Zeiss Measuring machine, increased
machine downtime, high levels of inventory and inventory turnover ratio, increased
scrap percent, poor housekeeping, improved inbound logistics but poor outbound
logistics. This put a question mark on their dedication and loyalty to the organization.
During the interview of the managers, it was discovered that two out of the five
managers whose children owned the ancillary were planning to leave the
organization. They wanted to focus on the growth of the ancillary.
2. One of the managers - the Purchase nager, was found to be at fault in his
record keeping upon a detailed enquiry it was found that he was making certain
purchases to gain personal benefits which were not in the interests of the company.
Because his children did not have any ancillary unit, therefore, he wanted to earn
money by dishonest practices. In a nutshell, the consultant explained
to Mr. Sen that the ancillary development shifted the direction of goals of the
managers away from the organizational goals. He explained to Mr. Sen the
behavioural model of organizational effectiveness in which organizational goals
must be reinforced by group and individual goals. Mr. Sen asked the consultant as to
why certain Japanese concepts which succeed in
practiced in some other country. The consultant replied that these concepts can
be applied in other countries after some modifications looking to the cultural
differences between
Action Plan : To prevent any further damage to India Gears, Mr. Sen decided to
terminate the services of some managers who had lost their loyalty to the company,
retrenched the dishonest Purchase manager and immediately gave an advertisement in
National newspapers for quickly recruiting and selecting new managers. He learnt a
lesson that copying the models of other countries could result in a disaster.
Questions :
(a) Which aspect of the Japanese Companies impress Mr. Sondhi ?
(b) Why did the starting of the ancillaries adversely affect the working of
Gears ?
(c) What were the findings of the consultant ?
(d) What was the action taken by Mr. Sen ?
Additional Info
- IGNOU books IGNOU books
Nalanda UNIVERSITY PGDFM AND PGDMM BOOKS FULLY SOLVED
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.com
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-I (Financial Decision Making)
NEW
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. What are finance funcitons? Explain.
2. Discuss the different types of investment decision.
3. Define leverage. Discuss its types.
4. Define Capital Structure. Discuss its components.
5. Define Dividend. Discuss the different forms of dividend.
6. Explain Walter’s dividend relevance theory.
7. What is Share? Discuss different types of share.
8. Discuss merits and demerits of debenture.
9. Define short term financing. Discuss trade credit as a spontaneous source of financing.
10. Define the concept of bank financing. Discuss the different forms of bank finance.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-I (Working Capital Management)
OLD
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. What do you mean by prime lending rate? How is it determined?
2. What is the differfence between gross working capital and net working capital? Describe the factors affecting determination of working capital.
3. What is working capital? Explain the components of working capital.
4. Discuss the internal and external factors affecting flow of cash.
5. Describe different aspects of working capital management.
6. Delineate the important components of receivable management system.
7. What is meant by 'Liquidity'? What factors affect liquidity? Explain the effects of liquidity.
8. Discuss the effects of inflation on working capital.
9. How does a bank provide credit to business units? Explain.
10. Why do firms hold inventory? Describe the components of an inventory system.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-II (Working Capital Management)
NEW
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. What is working capital? Discuss its importance.
2. Discuss in brief the different areas of working capital managements.
3. Discuss criterion for estimation working capital of any business firm.
4. Discuss the factors affecting working capital policy.
5. What is the role and need of liquidity in business? Discuss and explain the functions of cash management.
6. Discuss the merits and demerits of ‘too-liberal’ and ‘too-strict’ credit sales policy.
7. What are the main objectives of inventory management? How can a financial manager achieve these objectives?
8. Discuss long term sources of working capital.
9. What is a commercial paper? Discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
10. What is bank financing? Discuss the different forms of bank financing.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-II (Capital Investment and Financing)
OLD
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Examine the main principles of financial decisions.
2. Examine the factors influenceing financial engineering.
3. Write an essay on the development of banking sector in India.
4. Write an essay on Corporate governance and investor service.
5. Discuss the process of estimating cash flow for Capital budgeting.
6. What is dividend? What points should a company consider while determining dividend policy? Explain.
7. What is Control? What are its objectives? Throw light on the characteristics of a good control system.
8. What is lease finance? Under what circumstances it is cheaper than other sources of finance?
9. Define Company and describe its sources of finance.
10. Throw light on the importance of Capital market. What are its components? Explain.
![]()
![]()
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-III (Management Control System)
NEW
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. What do you understand by management control system? What are tis basic elements? Why management control system is important for an organisation?
2. Expalin the factors that affect design of management control system.
3. What do you mean by responsibility center? What are its nature and purpose?
4. Discuss different types of budgets in details.
5. Discuss in details various types of audits.
6. Describe various methods of project planning and scheduling.
7. What are the advantages of participative management? How the resistance to the participative management process be tackled?
8. Expalin different methods of transfer pricing.
9. Discuss break even analysis in detail.
10. Describe various techniques used in management control of operations.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-III (Management Control System)
OLD
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. Describe the features of a successful investment policy.
2. Discuss different aspects of corporate level strategy.
3. What do you mean by profit sharing system? Throw light on its objectives and mechanism.
4. For what reasons delegation of authority and assignment of responsibility are essential? Explain.
5. State the difference between Capital budgeting and revenue budgeting. What factors should be taken into consideration in connection with Capital budgeting?
6. Explain the framework of performance managemetn system.
7. What is investment centre? Describe its objectives.
8. Describe the nature, scope and objectives of management control system.
9. What is flexible budgeting? What are its limitations? Explain.
10. What is budgeting? Drow distinction between programme budgeting and performance budgeting.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-IV (Security Analysis and Portfolio Management)
NEW
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. What is investment? How it differes from speculation?
2. What is preference share? Throw light on different kinds of preference share.
3. Define secondary market and throw light on its relationship with primary market.
4. Explain various elements of settlement cycle carry forward system.
5. Discuss market inefficiencies of efficient market theory.
6. Explain various demensions of financial analysis.
7. Differential traditional portfolio analysis from modern portfolio analysis.
8. Discuss the significance of Beta in protfolio.
9. What do you understand by Capital Market Theory? Explain its assumptions.
10. Discuss the arbitrage pricing theory.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-IV (Security Analysis and Portfolio Management)
OLD
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. Discuss any one model of portfolio selection.
2. Examine critically the concept of mutual fund. How far mutual funds have been successful in India?
3. Wrtie an essay on the origin and growth of Stock Exchange market in India.
4. What do you mean by market efficiency? What are its different forms?
5. Exmaine the valuation methodologies generally used by investors of preference and equity shares.
6. Discuss various elements of investment environment.
7. What is meant by security? What are its different types? How security analysis is conducted?
8. What are the various concepts of portfolio return? Describe methods of calculating portfolio return.
9. Explain investmetn-decision process.
10. Discuss ‘DOW’ theory. What are its main features?
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-V (International Financial Management)
NEW
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Discuss the importance of International Financial Management.
2. Critically examine the role of World Bank in providing finance to multinational corporation.
3. Discuss the factors affecting exchange rate.
4. What is foreign exchange market? Discuss the participants of exchange market.
5. What is exchange rate? How is it determined?
6. Write an essay on currency options in India.
7. Discuss the different aspects of swap management.
8. What is the concept of FDI? Discuss the strategy for FDI.
9. Discuss financial and non-financial factors in capital budgeting.
10. Discuss the different aspects of cash management.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-V (International Financial Management)
OLD
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. What do you mean by international financial management? Describe its salient features.
2. Critically examine the comparative cost theory of international trade.
3. Discuss the impact of foreign exchange reserve and balance of payments on exchange-rate.
4. What is meant by multinational-corporation? Discuss its merits and demerits for a country like India.
5. Explain institutional arrangement of export and import finance in India.
6. Write an essay on the Debt-Crisis of Developing Countires.
7. What is 'Letter of Credit'? What is its importance in Financing Export Trade of a Country? Explain.
8. Throw light on the trends in India’s balance of payments in recent years.
9. Discuss the sources of institutional finance for growth of international trade.
10. Write notes on any two of the following:
|
(a) |
International Exchange Market |
|
|
(b) |
Foreign Direct Investment |
|
|
(c) |
Fixed and floating exchange-rate |
|
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-VI (Management of Financial Services)
NEW
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Distinguish between capital market and money market.
2. Explain meaning and concept of derivatives. Discuss trading framework of derivative market.
3. Define SEBI. Discuss its functions.
4. Describe in brief the financial services of financial institutions.
5. Define Marchant Bankers. Discuss the functions of Marchant Bankers.
6. Discuss the roel of Housing Development and Finance Corporation.
7. What is factoring? Discuss the types of factoring.
8. Describe in brief the methods of Venture Capital Financing.
9. What is stock exchange? Discuss the organisation and functions of stock exchange.
10. Discuss the role of international monetary fund.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management (PGDFM)
Paper-VI (Management of Financial Services)
OLD
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Discuss the impact of information revolution on financial services.
2. Discuss the role and need of regulations in a free market economy.
3. Throw light on the role of regulations in a free market economy.
4. Write an essay on rapid growth of Mutual Fund in India.
5. What are Financial Services? Describe various types of financial services.
6. Discuss the various strategies of managing risk.
7. Describe various steps in the process of portfolio management.
8. What are the functions of Stock Exchnage Market? Explain.
9. Define capital market and describe its participants.
10. What is insurance? Describe its objectives and functions.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 (Revised)
Post Graduate Diploma in Financial Management.

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
25/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -I |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
27/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –II |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
29/4/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –III |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
01/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –IV |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
03/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper –V |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
05/5/2017 |
|
PGDFM Paper -VI |
|
3.30 to 6.30 pm |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-I (Fundamentals of Marketing Management)
(NEW)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Define Marketing Management ? What are the importance of Marketing Management.
2. Describe the functions of a Marketing Manager.
3. Write an essay on the evolution of Marketing System.
4. Discuss the role of Corporate Sector in Marketing.
5. Define Branding. What are its advantages ?
6. Describe the role of discount, Rebate etc. in price determination.
7. Define retailer. Explain the different types of retailers.
8. What is marketing planning ? Explain the concept of market opportunity.
9. What do you mean by advertising decision and what are the different methods of advertising.
10. Write notes on any Two of the following :–
(a) Marketing Product and market choices
(b) Marketing Strategies
(c) Product Mix
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017
Post Graduate Diploma Courses
PGDMM

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
01/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-I |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
02/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-II |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
04/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-III |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
06/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-IV |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
08/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-V |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
10/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-VI |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c) Lifestyle Marketing |
|
|
|
(b) Cognitive dissonance |
|
|
|
(a) Self-Concept |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-I (Consumer Behaviour)
(OLD)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Explain the importance of consumer behaviour in marketing programmes.
2. How does an urban consumer differ from rural consumer in similar buying needs? Explain.
3. Discuss Trait theory of personality in the context of consumer behavior.
4. What is meant by subliminal perception? Explain the techniques of subliminal perception.
5. What is consumer attitude? Explain the inter-relationship among consumer attitude, beliefs and purchase intentions.
6. What do you understand by the term ‘Memory’? Explain its structure and functions.
7. What is the concept of learning? Describe the operant conditioning theory of learning.
8. Describe various models for study of Consumer behaviour.
9. What do you mean by buying decision? How does personality of consumer affect buying decision?
10. Write notes on any Two of the following :
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017
Post Graduate Diploma Courses
PGDMM

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
01/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-I |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
02/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-II |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
04/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-III |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
06/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-IV |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
08/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-V |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
10/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-VI |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-II (Consumer Behaviour)
(NEW)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry equal marks.
1. What do you mean by Consumer Behaviour ? Explain the importance of consumer behaviour in marketing programme.
2. What is Market Segmentation ? Explain the process of Segmentation.
3. What is meant by ‘Perception’ ? What factors influence perception ? Explain.
4. What do you understand by the term ‘Personality’ ? Explain the various determinants of personality.
5. How family life-cycle affects the Consumer Behaviour ?
6. What are the psychological factors affecting consumer buying behaviour ?
7. Explain the characteristic of Opinion Leadership.
8. Throw light upon Economic model of consumer behaviour.
9. What is Consumerism and discuss the changing role of women in assessing consumerism.
10. Discuss the main provision of Consumer Protection Act, 1986.
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017
Post Graduate Diploma Courses
PGDMM

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
01/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-I |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
02/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-II |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
04/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-III |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
06/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-IV |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
08/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-V |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
10/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-VI |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-II (Sales and Distribution Management)
(OLD)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Describe the qualities of a good sales personnel.
2. What is meant by 'selection'? Discuss the various tools of selection of salesman.
3. What are the objectives of communication? Explain written and verbal communication. What are the differences between the two?
4. Discuss the importance of training for sales personnel and explain training process in detail.
5. What is compensation? Discuss types of direct and indirect compensation.
6. Explain different types of sales quota. How quotas are fixed?
7. “Sales exhibition has become a focal poit in modern retailing.” Discuss.
8. What is job analysis? Throw light on the importance of job analysis for better management of sales force.
9. What are the components of strategy formulation in sales Management? Explain.
10. Write notes on any Two of the following :–
|
(a) |
Sales Management Audit |
|
||||||||
|
(b) |
B.D.I |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
(c) |
Compensation Package |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Post Graduate Diploma Courses |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
PGDMM |
|
|
|
||
|
Date |
|
|
Paper |
|
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
||
|
01/3/2017 |
|
|
PGDMM, Paper-I |
|
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
||
|
02/3/2017 |
|
|
PGDMM, Paper-II |
|
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
||
|
04/3/2017 |
|
|
PGDMM, Paper-III |
|
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
||
|
06/3/2017 |
|
|
PGDMM, Paper-IV |
|
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
||
|
08/3/2017 |
|
|
PGDMM, Paper-V |
|
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
||
|
10/3/2017 |
|
|
PGDMM, Paper-VI |
|
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
||
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-III (Marketing Cimmunication and Advertising)
(NEW)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. What is advertising? Highlight its importance.
2. What are the different types of corporate advertising?
3. What are the different types of sales promotion?
4. Compare comparative advertising in Australia and Argentina.
5. Discuss the role of creativity in marketing communication.
6. How will you allocate your advertising budget?
7. What are the departments of advertising agency?
8. Describe the process of DAGMAR.
9. Highlight the importance and relevance of marketing information systems.
10. Write notes on any two of the following :–
(a) Logical appeals
(b) Media planning
(c) Event marketing
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017
Post Graduate Diploma Courses
PGDMM

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
01/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-I |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
02/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-II |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
04/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-III |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
06/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-IV |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
08/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-V |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
10/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-VI |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-III (Product Management)
(OLD)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Explain the concept of Brand Equity and examine various methods of brand valuation.
2. Explain product obsolescence. What are its causes?
3. Describe sales forecasting. How can it be used for economic analysis of a new product?
4. Explain the term 'product-line' and 'product-mix'. What factors affect product-line decision?
5. What do you mean by product-mix? What factors influence change in product-mix?
6. Explain the concept of product portfolio analysis and throw light on its importance in decision-making.
7. What are the main objectives of price determination? Describe the methods of pricing.
8. What is product planning? Throw light on the traditional view point about product planning.
9. What is product life-cycle? Explain what measures can be taken for extending the life-cycle of a product.
10. Write notes on any two of the following :–
(a) Advertising strategy
(b) Shopping and speciality
(c) Test marketing
EXAMINATION PROGRAMME-2017
Post Graduate Diploma Courses
PGDMM

|
Date |
|
Paper |
|
Time |
|
Examination Centre |
|
01/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-I |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
02/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-II |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
04/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-III |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
06/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-IV |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
08/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-V |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
|
10/3/2017 |
|
PGDMM, Paper-VI |
|
8 to11 A.M |
|
Nalanda Open University, Patna |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-IV (Sales, Distribution and Retail Management)
(NEW)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksadsvad leku gSa A
1. What do you understand by recruitment and selection ? Discuss the sources of recruitment.
2. Describe various motivational theorics.
3. Discuss the relationship between channel management and the marketing mix.
4. What do you mean by Sales-person and Sales-force ? How these two have become so important in success of firm ?
5. Describe the characteristics of a Compensation plan ?
6. What do you understand by retail management ? What are the various types of retailers ?
7. Describe in detail about the foreign direct investment of retail in India ?
8. What is Store planning ? How it works ?
9. Describe in detail about Store employees evaluation ?
10. Write notes on any two of the following :–
(a) Electronic and non-store retailing
(b) Merchandise Management
(c) Store Management
|
(e) (c) Components of Political Risk |
|
(f) |
|
(g) (b) International Marketing and Foreign Trade |
|
(h) |
|
(i) (a) Cultural analysis of foreign market |
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-IV (International Marketing)
(OLD)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Define International marketing. What are its characteristics?
2. Write an essay on international advertising scenario.
3. Explain the main sources of funds available to an exporter.
4. Describe main import and export documents briefly.
5. Discuss the objectives and functions of International Monetary Fund (IMF).
6. Draw distinction between the following :
(a) Global and Domestic Marketing
(b) Direct and Indirect Distribution Channel
7. Explain various combinations of Communication Strategies available of global market.
8. Discuss the impact of export-import policy on international marketing.
9. What do you understand by international marketing research? Explain its scope.
10. Write notes on any two of the following:
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-V (Marketing of Services)
(NEW)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. Discuss the technological support for effective services marketing.
2. What is the role of CRM (Customer Relationship Management) in delivering a customer relationship strategy?
3. What do you mean by developing services for specific segments? What is the distinction between important and determinant attributes in consumer choice decisions?
4. Explain the basic services package. Discuss its essential elements.
5. Explain criteria for good service quality.
6. Discuss the pricing implications of different cost analysis.
7. Describe the role of personal selling in service communications. Give examples of three situations in which you have encoutered this approach.
8. Explain the importance of e-commerce in the field of service distribution.
9. Explain marketing mix as a tool of marketing strategy.
10. Write notes on any two of the following:
(a) Micro Segmentation
(b) Objectives of Service Pricing
(c) Location and Time of Delivery
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-V (Marketing of Services)
(OLD)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. What do you understand by international marketing of services? Explain the measures for promoting international marketing of services.
2. Discuss the relevance and role of 'Physical Evidence' in marketing of services.
lsokvksa ds foi.ku esa ^HkkSxksfyd izek.k* dh izklafxdrk vkSj Hkwfedk dh foospuk dhft, A
3. Explain the term 'yield management' and discuss the importance of yield management for hotel industry.
4. Explain the factors affecting the determination of prices of services. How price determination of services differs from price determination of goods?
5. Discuss the changing scenario of Indian Banking Industry.
6. Write an essay on the contribution of service sector to India’s international trade.
7. What is the nature of trousim as a service industry? Describe the factors affecting demand and supply of tourism.
8. Explain consumer behaviour in the context of financial services. Explain influence of family on buying behaviour.
9. "Services have a number of unique characteristics that make them different from product." Discuss this statement.
10. Write note an any Two of the following :-
(a) International marketing and Interactive marketing
(b) Core services and Supporting services
(c) Experience quality and Credence quality
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-VI (International Marketing)
(NEW)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
1. Explain the benefit of International Marketing.
2. What is political environment ? Is it country specific, firm specific or both ? What are its major components ?
3. Differentiate between a free trade area and a common market. Explain the marketing implications of the diffeences.
4. Explain the role of analysis of Entry Strategies.
5. What were the purposes for which IMF and world Bank were established ?
6. What do you mean by Market Research ? Discuss its nature and scope of marketing research.
7. Explain in brief the functions of the World Trade Organisation. What are the major principles of multilateral trading system ?
8. Discuss the export-import procedures.
9. What is the role of a service institutions in international trade ? Comment.
10. Write notes on any two of the following :–
(a) European Monetary System
(b) Research Design
(c) Import licening procedures
Nalanda Open University
Annual Exam-2017
Post Graduate Diploma in Marketing Management (PGDMM)
Paper-VI (Management of Marketing Communication & Advertising)
(OLD)
Time: 3.00 Hrs. Full Marks: 80
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry euqal marks.
fdUgha ik¡p ç'uksa ds mÙkj nhft, A lHkh ç'uksa ds vad leku gSa A
1. Describe the characteristics and advantages of direct marketing.
2. What are the advantages of print media and television for a hotel proprietor of
national repute? Discuss.
3. What is meant by marketing communication? Throw light on its importance and
advantages.
4. What is the difference between sales promotion and personal selling? Explain the situations under which sales promotion schemes and personal selling are more effective than mass media advertisement.
5. Define innovation and creativity and throw light on their respective features.
6. What do you mean by creative association? Describe various kinds of creative association with examples.
7. Describe the changes taking place on the horizon of Indian media in recent years.
8. What is meant by public relations? Distinguish between public relations and
advertising.
9. How does promotion differ from marketing communication? Explain elements of promotion mix.
10. Write shorts notes on any two of the following:
(a) Message Design and positioning
(b) Positioning of Advertising Agency
(c) Social Marketing Communication
Ignou pgdibo assignments 2018-19
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.com
Ignou Pgdibo assignments , IGNOU IBO-01,02,03,04,05,06 , IGNOU ASSIGNMENTS FROM pgdibo , ignou pgdibo assignments from ignou university
TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT
Course Code : IBO – 01
Course Title : International Business Environment
Assignment Code : IBO – 01/TMA/2018-19
Coverage : All Blocks
Maximum Marks: 100
Attempt all the questions.
1. Why is transfer of technology required? Describe various non-equity forms of
technology transfer by TNCs and Small and Medium Enterprises.
(5+15)
2. (a) Describe the problems of developing countries related to the world trade.
(b) Examine the impact of Regional Economic Grouping.
(10+10)
examples.
b) A seller can not convey a better title than that at his own. Discuss and describe
the exceptions of this rule.
4. Comment on the following:
(i) There is no relevance of international business environment.
(ii) There has been no effect of globalization on the world economy.
(iii) The Asian Development Bank does not give special attention to the needs of
the smaller or less developed countries.
(iv) There are no difference between ethical dilemmas and ethical lapses.
(10+10)
(5x4)
5. Write short notes on the following:
(i) UNCTAD and Commodities
(ii) Areas of International Trade Disputes
(iii) Business and Social Responsibility
(iv) Convention on International Trade in endangered species of wild Fauna and
Flora (CITES)
(5×4)TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT
Course Code : IBO – 02
Course Title : International Marketing Management
Assignment Code : IBO – 02/TMA/2018-19
Coverage : All Blocks
Maximum Marks: 100
Attempt all the questions.
1) A) Distinguish between the following:
i) International Marketing and Multinational Marketing
ii) Probability Sampling and Non-probability Sampling
(2x5)
B) Write short notes on the following:
iii) EPRG Orientation
iv) International Promotion Mix
(2x5)
2) Explain the various steps involved in the international market selection.
(20)
3) Differentiate between product standardization and adaption in the internal marketing. Evaluate
the various factors of standardization and adaptation, and suggest the conditions under which
each of them is applicable.
(5+15)
4) “Compared with products, marketing of services posses distinctive challenges to international
marketers”. Explain why it is so. Enumerate the barriers to international marketing of services.
(8+12)
5) Explain the key decisions in international marketing communications.
(20)TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT
Course Code : IBO – 03
Course Title :
Assignment Code : IBO – 03/TMA/2018-19
Coverage : All Blocks
Maximum Marks: 100
Attempt all the questions.
1. What is the meant by balance of payments? How is it classified? Explain salient features
of
(4+4+12)
2. Describe various constraints hampering effective export promotion efforts in
(20)
3. “The gems and jewellery sector is one of the highest foreign exchange earners for the
country.” Elaborate.
(20)
4. Comment on the following statements;
(a) The chemical industry has recorded an impressive growth in exports during the last
few years.
(b)
(c) In recent years,
in the realization of its economic growth.
(d) ASEAN region is important to
(4×5)
5. Write short notes on the following:
(a)
(b) Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
(c)
(d) Trade prospects between
(4×5)TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT
Course Code : IBO – 04
Course Title : Export Import Procedures and Documentation
Assignment Code : IBO – 04/TMA/2018-19
Coverage : All Blocks
Maximum Marks: 100
Attempt all the questions.
an FOB contract? Discuss with example and explain the legal implications of FOB and
CIF contracts.
b) Describe the general conditions in export contracts. (10+10)
b) Explain different kinds of letter of credit. (10+10)
3. Why should the export goods be insured? Describe various types of losses under cargo
insurance with examples. (5+15)
4. Comment on the following statements:
a) Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has no role in business.
b) From the exporter’s point of view, advance payment is free from any kind of credit or
transfer risks.
c) Under bare - boat charter the ship owner do not let out the bare ship for a period of
time.
d) In
effort. (5x4)
5. Write short notes on the following:
i) Port procedures
ii) Exchange control regulations concerning imports
iii) Chartering practice
iv) Duty drawback scheme (5x4)TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT (TMA)
Course Code : IBO-05
Course Title : International Marketing Logistics
Assignment Code : IBO-05/TMA/2018-19
Coverage : All Blocks
Maximum Marks: 100
Attempt all the questions.
1. (a) Discuss the various types of surcharges that are usually levied on the basic freight rates.
(b) How is the time charter different from bare boat charter? (10+10)
2. What is economic exposure? Explain the method of market initiative as a hedging technique of
economic exposure. (20)
3. Differentiate between the following:
(a) Ship Owner’s Lien and Maritime Lien
(b) Air transport and Rail Transport
(c) Heavy Lift Surcharge and Long Lift Surcharge
(d) Re-order Level (ROL) and Re-order Quantity (ROQ) (5x4)
4. Write short notes on the following
(a) ABC Technique
(b) Tank Container
(c) Voyage Charter
(d) International Chamber of Commerce (5x4)
5. Briefly comment on the following:
(a) Cross subsidization is the characteristics feature of the liner freight.
(b) Bill of Lading is a document of title to goods.
(c) Application for registration is made by the ship owner.
(d) Controlling inventories are vital in the logistics activity mix. (5x4)TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT
Course Code : IBO – 06
Course Title : International Business Finance
Assignment Code : IBO – 06/TMA/2018-19
Coverage : All Blocks
Maximum Marks: 100
Attempt all the questions.
1. Discuss the main function of the IMF. Explain and compare the gold standard Bretton
woods systems. (8+12)
2. (a) Discuss the Forex Market structure in
(b) Evaluate the developments in the Forex Market in
3. (a) Explain what kind of risks in Foreign Exchange are faced by the MNCs.
(b) Explain the mechanism of money market hedge for accounts receivables. (10+10)
4. (a) How do you think that cost of capital and capital structure are interrelated?
(b) What factors differentiate the determination of cost of capital and capital for a MNC as
compared to a domestic firm? (10+10)
5. (a) What do you understand by counter trade? Mention few circumstances where counter
trade can be beneficial for a country.
(b) “Letter of Credit makes financing of Receivables easy” – Comment. (10+10
MS-22 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-22 : HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : There are two Sections A and B. Attempt any three questions from Section A. Each question carries 20 marks. Section B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION – A
1. "With global economy and the world becoming a global village, the business enterprises have became extremely cautious of the need for hiring competent human resources and developing core competencies for every organisation." Elaborate this statement and discuss the underlying concept and process, with example.
2. What is Action Research ? How does it differ from OD ? Discuss the important factors to be considered in development of internal self-renewal facilitators, with suitable examples.
3. How does HRD Audit help development process of an organisation ? Explain the concept and discuss how HRD Audit is conducted in an organisation.
4. How does HRD help managing technological changes ? Discuss the role of HRD in developing the changed mindset. Justify with suitable example.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) 360 0 Appraisal
(b) Mentoring
(c) Role of Trade Unions in HRD
(d) Career Transition and Choices
(e) Horizontal re-skilling
SECTION - B
6. Read the case given below and answer the questions given at the end.
The National Transport Corporation (hereinafter referred to as NTC), a leading transport organization with a fleet strength of 200 vehicles, is engaged in Parcel Services in South India. The NTC has its headquarters at Madras, and has branches in important locations in Tamil Nadu and other southern states.
Madhavan, a loadman of NTC at Salem, was transferred from Salem to Madura, for long absence from work in the beginning of 1985, though the corporation could have discharged him from service for long absence without permission, for a period of two months. The Branch Manager of Salem, NTC requested the Head of the Human Resources Division to transfer the employee to another location, to enable the employee to correct himself in future. Madhavan was in NTC from the beginning of 1982.
Madhavan reported for duty at Madura, and again after six months of service, started absenting from work as before. The Branch Manager of Madura counselled him several times, but Madhavan did not show any real change in his attitude. A written warning was given to him in October 1985. He again absented himself from duty on 17th December, 1985 for ten days, and after joining duty on 15th January, he was again absent for 10 days. Disciplinary action followed.
At the departmental enquiry held in February 1986, Mr. Madhavan pleaded that he was suffering from jaundice and that he rushed to his village near Salem for taking Ayurvedic treatment and rest. No medical certificate was produced. He admitted his mistake in not applying for leave, to the enquiry officer and requested for mercy.
Based on the admission of the misconduct, the enquiry officer gave the findings that he was guilty. The Branch Manager, Madura was informed about the findings. He recommended dismissal (for provisions refer to Anrtexure-A)
The Chief Executive of NTC, the punishing authority, took the decision that the delinquent was not willing to work regularly. He, however, again directed a transfer to Madras, rather than passing an order of dismissal. This was done, once again, to enable the employee to correct himself.
Before issue of orders, Mr. Madhavan approached the Chief Executive of NTC and requested for mercy. He was not in favour of changing the order of transfer. He, however, referred the matter to the Manager of the Human Resources Division for proper disposal.
The Manager HRD, asked Madhavan, the reasons for absence. He asked Mr. Madhavan how a company would tolerate such absenteeism. He was asked why he failed to produce medical certificates, if he was really sick ? Was he not given an opportunity twice to correct himself, once by the Branch Manager, Salem and later by the Branch Manager, Madura ? Madhavan had no answer to these questions. He, however, requested the Manager to give him one last chance. He had no complaints against the Branch Managers. The management assured support to him if his version was convincing. Madhavan then narrated his family background.
Madhavan's Family Background
He was born to Gundappan and Palaniammal. He had two eldei sisters, four elder brothers and another brother younger to him. His sisters and two brothers were living separately after marriage. He got the job as a loadman in NTC in 1982 at Salem, through his brother-in-law, another senior loadman at NTC. Another unmarried brother of his, aged 33 was employed in a hotel and was living separately. He was living with his parents, a disabled brother aged 35 and his younger brother at Kamandapatti (Please refer Annexure-B) till the end of 1984 in the family house. He was the bread winner of the family.
Madhavan was now living at Omalur, with his wife Madhavi aged 22. Madhavi's tale was a tragic one. A native of Taramangalam, 10 kms, from Omalur, her father was in the military, and was now no more.
She was married in 1983 to her father's sister's son Gopal. However, she was ill-treated by both her in-laws and her husband and deprived of her ornaments. Disillusioned, she applied for a divorce and got an alimony of !. 2,000. This helped her to establish a small grocery shop at Omalur and settling down with
her sister's family.
Here Madhavan developed intimacy with Madhavi much to the dislike of her sister, and another Gunapalan, a person known to Madhavan. Gunapalan wanted to marry Madhavi. But Madhavi had no interest in him. Gunapalan in this background posed serious problems to Madhavi especially after Madhavan's transfer to Madura. Gunapalan was determined to win her hand. He told her twice that she will have to forget Madhavan, or else she will have to blame herself for the consequences. Threats
followed.
Madhavan got a letter from Madhavi. She wanted real protection. She had antagonized Gunapalan and could not completely rely on her married sister. They should marry - she wrote to him. Madhavan reached Omalur to see that Madhavi's shop was burgled by unknown persons. There was a rumour in the air that GUnapalan was behind everything
Madhavan decided to marry Madhavi. He married her from the Madura Temple and later went on a pilgrimage for a fortnight. He, however, did not inform the NTC officials and employees about his marriage. He never applied for leave as well during the marriage on 6th January, 1986. What followed was the disciplinary action against Madhavan and his entreaty against transfer.
Madhavan gave a definite undertaking to the Manager that he would be diligent in the work in future and that the management could terminate his services, upon any complaint in future.
The Manager (HRD) contacted the Branch Managers of Madura and Salem and took them into confidence. The family background was fully explained to both the Branch Managers. It transpired that Madhavan had never explained his problems to either of them. Both Managers agreed to abide by the decision of the Manager (HRD) to help the employee concerned. Both promised to counsel Madhavan as well, if he was posted either at Madura or Salem
The Manager (HRD) taking into account his family background passed an order transferring the employee to Salem.
Questions :
(a) What should be your stand on this issue as the Head of HRD Division of the organisation, viewing the problem in the area of Human Resources Development to correct the employee ?
(b) Do you think that the employee cannot be corrected as he has absented continuously for long periods while at Salem and Madura and that sympathy shown to him will amount to a premium on indiscipline, adversely affecting the corporate image of the organisation and the employee ?
(c) Are you of the view that it is possible to correct him by the theory of constructive discipline and if so, how ?
(d) Are you of the view that if you transfer him to his home town, Salem, Madhavan would prove himself to be a good performer as he will be in a position to discharge his duties as an employee and as a sincere family member ?
Annexure – A Provisions in Standing Orders
Habitual absence without leave or absence without leave for more than 10 days. Habitual late attendance.
Punishment - An employee who is found guilty of a misconduct may be punished as provided herein, depending upon the gravity of the misconduct committed by the employee.
(a) Fine, up to 2% of monthly salary
(b) Warning
(c) Demotion
(d) Stoppage of increment
(e) Suspension for 30 days
(f) Discharge or dismissal
The management has the right to transfer employees from head office to branches and vice versa for exigencies of service.
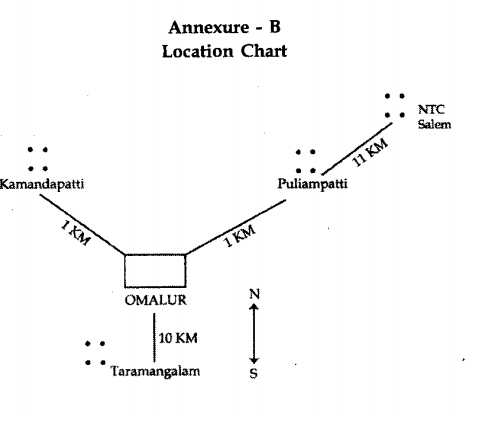
MS-21 December,
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
December, 2015
MS-21 : SOCIAL PROCESSES AND BEHAVIOURAL ISSUES
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 (Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) There are two Sections A and B. (ii) Attempt any three questions from Section - A. All
questions carry 20 marks each.
(iii) Section - B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
1. What are the strategies available to a manager in an organisational set to enhance employee motivation ?
2. Briefly describe the components of Emotional intelligence and its importance in organisations. Can emotional intelligence be learnt ? Discuss in brief.
3. Briefly discuss different group decision makingtechniques and their strengths and weakness.
4. Describe Johari Window Model and Transactional analysis. Discuss how these models help in strengthening interpersonal relations ?
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Qualities of an effective Counselor.
(b) Preventing Inter-group conflict.
(c) Referrent Power.
(d) Characteristics of Learning organization
(e) Cultural Shock.
SECTION - B
6. Read the following case carefully and answer the questions given at the end :
Dharam Singh, general manager at 'Prithviraj Chemicals' was worried about his future, even though he had been told that after 'Prithviraj Chemicals' is merged with Orchid Pharmaceuticals he would be promoted and also be required to shoulder the additional responsibility of identifying those who should be retained as employees even after the merger. Dharam was concerned because he had heard that the organisational culture at 'Orchid' was computer driven, while at 'Prithviraj Chemicals', the focus was on "relationship"
A month later after the official merger of the two companies, the new management took the decision to shift the headquarters to Bangalore from Mysore. This decision was communicated to its employees, (many of 'Prithviraj Chemicals'). They approached Dharam Singh to ask 'Why was the new management shifting its Headquarters to a new place (Bangalore)', Was it because the two managements did not trust each other ?' This question was posed especially because most of Prithviraj's employees had become used to the'quiet, risk averse and friendly work environment' and were worried whether in Bangalore, with its 'cosmopolitan outlook, it would lead to cultural clashes.
As anticipated there were certain instances which had Dharam Singh wondering how to solve such cultural differences. The 'Prithviraj employees' consensus, relationship-result oriented approach always believed in an open communication system with all employees keeping each other informed about any decision and bringing about a consensus in all the decisions taken. On the other hand, the 'Orchid' employees were individually only concerned with their 'individual' work i.e., they were more focused on ambitious cost-cutting goals and each employee was individually responsible for quantifiable results.
• Whenever any work related problem arose,the 'Prithviraj' employees adopted an attitude 'Tell us about the problem from all angles and we will discuss and tell you how best to handle it.' In contrast, the 'Orchid' employees attitude was 'just tell me how this problem will/may affect my work, I am not interested in the whole problem.
. Many of 'Orchid' employees had worked in other cities of North India and few of them had also travelled abroad for official work and thus were more confident, more computer savvy, tough and didn't mince words. Because of this, the 'Prithviraj' employees felt threatened and preferred to describe 'Orchid' employees as 'loners','tough' and 'hard working.'
• At 'Prithviraj', employees were required to make weekly financial and staffing updates to their 'bosses'. However, at 'Orchid' this formality was considered to be a waste of time and they didn't adopt or accept this practice.
Dharam Singh had been with 'Prithviraj since the last 12 years and knew that 'Sudhir' (the M.D. at 'Prithviraj') had a lot of confidence in him when he had said "Dharam, I am very sure that we can count on you to see that there is no dissent among the employees after the merger. The new company is looking upon you to solve the societal-level cultural difference which is prevailing among the employees, so that we can have our own unique culture which would be a blend of both 'Prithviraj' and 'Orchid's way of doing business."
Questions :
(a) Critically analyse the core issues of the case.
(b) Understanding the type of culture followed by 'Prithviraj' and 'Orchid', what type of culture should the newly merged company follow ?
(c) Can you suggest ways to help Dharam Singh to cope with the existing cultural differences ?
MS-11 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-11 : STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) There are two Sections : Section-A and
Section-B.
(ii) Answer any three questions from Section-A.
All questions in Section-A carry 20 marks each.
(iii) Section-B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
(a)Differentiate strategy with policies and tactics giving examples.
(b)Differentiate strategy with programmes, procedure and rules giving examples.
2. (a) What are different types of differentiation ? Explain each of them with the help of examples.
(b) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of differentiation.
3. Describe Porter's five forces framework as the most widely used tool to analyze the competitive
environment.
4. What do you understand by 'International Expansion' ? Discuss the different ways through
which expansion into foriegn markets can be achieved.
5. Write short notes on any two of the following :
(a) Forms of organisation structure.
(b) Strategic alliance.
(c) Dimensions of leadership styles.
(d) Value chain.
SECTION - B
6. Read the following case and answer the questions given at the end.
CASE STUDY : SAMSUNG & APPLE : A UNIQUE PROPOSITION
Apple Inc sued Samsung Electronics claiming the South Korean firm's Galaxy line of mobile phones and tablets "slavishly" copies the iPhone and iPad, according to court papers, a move analysts say is aimed at keeping its close rivals at bay
Apple is one participant in a web of litigation among phone makers and software firms over who owns the patents used in smart phones, as rivals aggressively rush into the smart phone and tablet market which the US firm jumpstarted with iPhone and Wad.
Nokia has also sued Apple, which in turn has sued Taiwanese handset maker HTC Corp.
Samsung is one of the fastest growing smart phone makers and has emerged as Apple's strongest competitor in the booming tablet market with models in three sizes but it remains a distant
second in the space.
Its Galaxy products use Google Inc's Android operating system, which directly competes with Apple's mobile software. However, Apple's claims against Samsung focus on Galaxy's design features, such as the look of its screen icons, the lawsuit said.
John Jackson, an analyst with CCS Insight, said Samsung is essentially Apple's only real tablet competitor at this stage. "It's clear that they do not intend to let Apple run away with the category", Jackson said
Samsung faces the challenge of moving beyond being a hardware company, clever at copying ideas, to becoming more creative, better adept at software, at a time when consumer gadgets are getting smarter all the time.
It has yet to come up with the kind of original, iconic, market-leading products that powered brands such as Apple's i-series or Sony Corp's Walkman. Nor has it taken the kind of initiatives in software that Google and Apple did to thwart Microsoft.
The lawsuit, field on Friday, alleges Samsung violated Apple's patents and trademarks.
"This kind of blatant copying is wrong", Apple spokeswoman Kristin Huguet said in a statement.
Samsung said it would respond to the legal action "through appropriate legal measures to protect our intellectual property."
"Samsung's development of core technologies and strengthening our intellectual property portfolio are keys to our continued success," it said in a statement.
Retaliation
Hit by a lawsuit from Apple last week, Samsung returned the favor yesterday, countersuing the iPhone and iPad maker over claims of patent infringement.
In its suit filed in Seoul Central District Court, Samsung claims that Apple is violating five different patents. Samsung has also field a suit in Tokyo, citing two patent infringements, and another in Manheim, Germany, citing three instances of infringement.
A statement on the Samsung Web site says that the company is "responding actively to the legal action taken against us in order to protect our intellectual property and to ensure our continued innovation and growth in the mobile communications business."
Symbiotic Relationship
Apple has reportedly become Samsung's biggest customer in a move that can boggle the mind. How can Apple, a rival of Samsung's electronics unit, also be the largest customer ? And how long can this scenario go on ?
According to the Korea Economic Daily, Apple is poised to buy $7.8 billion in components from Samsung. These components range from liquid crystal displays, application processors and flash memory used in the iPhone and Pad.
If you bring this up in conversation, the Apple - Samsung relationship can become a headscratcher. Apple's iPhone battles Samsung's Galaxy phones. The Galaxy Tab takes on the iPad. Meanwhile, Samsung's tablets can't match the iPad on price - even though the Korean electronics provider has many parts lying around the company
How is this Apple - Samsung thing even possible ? Apple certainly wouldn't sell components to Samsung if the roles were reversed. If you carry this line of thinking out to an extreme Apple could squash Samsung with its own parts. It's strange.
Questions :
(a) Describe the strategies adopted by Apple to become the leader in the smart phone market.
(b) How can Samsung Electronics Counteract Apple to capture the market ? Explain with relevant R and D strategy that it can persue.
MS-10 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-10 : ORGANISATIONAL DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND CHANGE
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 (Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) There are two Sections A and B.
(ii) Attempt any three questions from Section-A. All questions carry 20 marks each.
(iii) Section-B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
1. What is Organizational Development (OD) ? Describe various stages of OD and their relevance.
2. Differentiating organization and institution, describe what characterizes an institution and factors influencing institution building.
3. Describe any two diagnostic tools and their advantages and disadvantages.
4. Distinguish between job, occupation, and career and discuss any two approaches of job design and their merits and demerits.
5. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Hybrid Structure
(b) Time and Motion Study
(c) Process Consultation
(d) Process of Change
(e) Organisations as Political Systems
SECTION - B
6. Read the following case carefully and answer the questions given at the end :
Since 1994, Boeing began the process of remaking the company for the next round of aircraft purchases. Every part of the company is involved, from engineering to manufacturing. The focus of the change is that Boeing is a manufacturing company rather than an engineering and technology company. Due to changes in the air travel business, the major commercial airlines are demanding lower airplane prices and significantly lower operating costs. Airbus continues to be a fierce competitor, so Boeing must meet the competition early and on every front. (Boeing bought Mc Donnell Douglas in 1997.)
It is not as if the company is in financial trouble. Its new model 777 is generating lots of orders. Plans are in the works for a new supersonic and another jumbo jet for commercial sales, and several new project possibilities exist for the defence division. The new 777 was designed completely on the computer so that designs went straight from the designer'scomputers to the machine tools for manufacturing. It can carry as many as four hundred passengers, fifty more than the comparable Airbus 33 t. It is 15 per cent more fuel efficient, and can fly over eight thousand miles non-stop. Orders are coming in faster than
for any other new plane, although its price is pretty steep : $12 - $15 million, depending on
interior layout.
Boeing's new CEO, Philip Condit, must continue the reductions in cycle time and cost cutting, started by his predecessor, Frank Shrontz, because airlines are making their purchase decisions differently than in the past, even choosing in some cases to refurbish older planes rather than buy expensive new ones. The changes started with Condit and his team of presidents of the divisions of commercial planes, defence and space, and computer services. This group differs notably from its predecessors in that they have met together for several years to discuss the good and bad things about each other's divisions and
the future of the company. They all embrace the new togetherness theme as the primary means
through which the company will be able to reduce cycle times, improve delivery times, cut product
development time, and reduce total costs.
In the former structure the design and manufacturing groups were separate. Design and engineering groups would design the planes and then give the plans to manufacturing to build. When problems existed in the design, they would be sent through the hierarchy back to engineering for correction. Under the new structure, comprehensive design-and-build teams include members of all groups involved. Therefore, planes are originally designed to meet customer's needs, are easier to build, and corrections are made faster. For example, previously, when tool builder Tony Russell had a problem with an engineering design or specification, he would have to go to his supervisor and the problem would be shuffled through to engineering. Now he goes directly to the engineering and design group, gets the problem solved, and gets back to work with the correct design. This type of revision in the process
has helped reduce the product delivery time from eighteen to ten months. The team approach and working-together ideas were used extensively on the 777. Some teams included tool makers, designers, manufacturing workers, suppliers, and even customer representatives. Contrary to past procedures, workers on the line were allowed to change how planes were built, which has significantly decreased costs. Condit has instituted 360 degree performance reviews in which managers are evaluated by their subordinates, their peers, and their own supervisors to improve understanding of how they are doing from all perspectives. Employee empowerment is increasing at all levels. Condit and his team are having quite an impact throughout the company.
Questions :
(a) The new way of organizing at Boeing most resembles which of the classical types of organizing ? Justify.
(b) How have responsibility and authority been altered under Condit's new approach ?
(c) Describe the new ways of organizing at Boeing in terms of the configurational and operational aspects of structure
MS-9 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-9 : MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
Note : (i) There are two Sections : Section-A and Section-B.
(ii) Attempt three questions from Section-A carrying 20 marks each.
(iii) Section-B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
1. Explain the equi-marginal principle. Elucidate with the help of examples.
2. Discuss any five variables, which can be included in the demand function and can have a major impact on the demand.
3. Explain the production function with two variable inputs i.e. production isoquants giving examples.
4. What is Oligopoly ? Explain the important characteristics of Oligopoly.
5. Write short notes on the following :
(a) Bundling
(b) Cartels.
SECTION - B
6. Assume a firm has the following total revenue and total cost functions :
TR =320Q — 2Q2
TC =1800 +50Q + 3Q2
Determine :
(a) The level of output at which the firm will be maximizing profits ;
(b) The level of output at which total revenue will be maximum.
7. (a) Explain why a firm facing a downward sloping demand curve would never produce the inelastic (ep < 1) portion of the demand curve.
(b) When would the firm operate at the point where demand curve is unitary elastic ?
MS-8 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
MS-8 December, 2015
MS-8 : QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS FOR MANAGERIAL APPLICATIONS
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) Section A has six questions, each carrying 15 marks. Attempt any four questions from this
Section.
(ii) Section B is compulsory and carries 40 marks. Attempt both questions.
(iii) Statistical tables may be supplied on request.
(iv) Use of calculator is permissible.
SECTION - A
1. A person pays a total of Z 975 through monthly installments each less than the former by Z 5. The
first installment is ! 100. In how many installments will the amount be paid ?
2. Calculate the harmonic mean from the following frequency distribution :

3. The incidence of a certain disease is such that on an average 20% of workers suffer from it. If 10 workers are selected at random, find the probability that :
(a) Exactly two workers suffer from the disease.
(b) Not more than 2 workers suffer from the disease.
4. Explain the meaning of sampling distribution of a sample statistic. Obtain the sampling distribution of mean in case of sampling from infinite populations.
5. A company wants to study the relation between R and D expenditure (X) and sales (Y) for the ten-year period. Determine the correlation coefficient between these variables.
6. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Identity matrix
(b) Quantiles
(c) Axioms of probability
(d) The power curve of a test
(e) Mixed Auto-regressive - moving average models
SECTION – B
7. The mean life of a sample of 10 electric bulbs was found to be 1456 hours with a standard deviation of 423 hours. A second sample of 17 bulbs chosen from a different batch showed a mean life of 1280
hours with a standard deviation of 398 hours. Is there a significant difference between the meansof the two batches ?
8. What is skewness ? Distinguish between Karl Pearson's and Bowley's coefficient of skewness. Which one of these would you prefer and why ?
MS-7 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-7 : INFORMATION SYSTEMS FOR MANAGERS
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : Answer any four questions. All questions carryequal marks.
1.(a) What is the purpose of a TPS ? How does itcompliment MIS in an organisation ?
(b) Discuss some of the benefits of using a Firewall for the LAN.
2.(a)What are the various ways of assessing the value of information ? Explain any one method briefly.
(b)What impact does the implementation of programmed decision - making have on the management system of an organisation ?
3. (a) Discuss the use of computers in decision - making for Human Resource Management.
(b) Give reasons for the statement - "Information Systems Contribute to Total Quality Management".
4. (a) What is Outsourcing Information System ? List its advantages and disadvantages.
(b) What are the phases of traditional system life cycle where users are highly involved ?
5.(a) What are expert systems ? Mention the working principles of expert systems.
(b) In context of a data warehouse, what is a concept hierarchy ?
6.(a) Discuss the competitiveness of ICT with respect to modern business practices.
(b)Highlight the impact of ICT for developing nations with respect to the economic activities.
More...
MS-6 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
MS-6 : MARKETING FOR MANAGERS
December, 2015
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) Attempt any three questions from Section-A.
(ii) Section-B is compulsory.
(iii) All questions carry equal marks.
SECTION - A
Explain the three additional elements in the marketing mix specifically required for services.
What is market segmentation ? Suggest suitable bases for segmenting the markets
for the following products :
(i) Toothpaste
(ii) Biscuits
2. (a) Discuss the major areas of application of marketing research.
(b) Explain the functions of packaging with
reference to : •
(i) A fast moving consumer good
(ii) An industrial product
3. (a) What is cyber marketing ? How is it different from conventional marketing ? Explain
giving examples.
(b) Explain the need for non-financial motivation for salespersons and mention some of the ways through which this can be achieved.
4. Write short notes on any three of the following :
(a) Relevance of social marketing
(b) Methods of designing the marketing organisation
(c) Cultural factors affecting consumer
behaviour
(d) Pricing methods
(e) Stages in the buyer dicision process
SECTION - B
5. Study the case given below and answer the questions given at the end.
Office Needs is a marketer of good-quality office furniture, carpets, safes and filling cabinets. Within each category, the company offers a wide variety of products with a great many variations of each, product being offered. For instance, the company currently offers around 42 different designs of chairs and 23 varieties of office desks. The company keeps in touch with advances made in the office furniture field worldwide and introduces those products which are in keeping with the needs of the market in terms of design, workmanship, value for money and technical specifications.
Office Needs trades only in quality furniture which is sturdily constructed. Differences between its products and cheaper, lower quality ones are well known to those who have several years of experience in the business.
An important feature, the company feels, is the availability of a complete list of components of the furniture system. This enables the customer to add bits and pieces of matching designs and
colour in the future. Such components are available for sale separately. Systems are maintained in stock by the company for a number of years, and spare parts for chairs and other furniture are always available.
The trade is currently witnessing a downtrend due to recession and players from local unorganized sector. Office Needs has also experienced the same over the last two years. In addition, it had to trim the profit margins. Last year, it barely broke even and this year it is heading for a small loss for the first time in the company's ten year history
Questions :
(a) Explain the terms Product Item, Product Line and Product Mix in the context of the above situation.
(b) What strategy would you recommend to counter competition from the unorganized sector ?
(c) Suggest a suitable promotion strategy for the company.
MS-5 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-5 : MANAGEMENT OF MACHINESAND MATERIALS
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 (Weightage 70%)
Note : (i) Answer any four questions.
(ii) All questions carry equal marks.
1. (a) Explain the importantce of Management of materials in production system in modern
manufacturing industry.
(b) Distinguish between Strategic Decisions and Operational Decisions. Discuss.
2. (a) Describe the major quantitative models used for facility location.
(b) Briefly explain the 'continuous flow process'. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of a continuous flow process.
3. (a) Describe the work measurement procedure. Discuss the major techniques of work measurement.
(b) "Environmental factor is necessary in modern industry." Do you agree ? Explain with examples.
4. (a) Describe 'Kilbridge - Wester' method and 'Helgeson - Birnie' method.
(b) How maintenance system can be profitable in a large -scale industry ? Discuss the various types of maintenance systems.
5. (a) What is value engineering ? Discuss its importance.
(b) Distinguish between 'quality control', 'quality assurance' and 'total quality management.'
6. (a) Describe the technique of 'economic order quantity'. Derive classical economic order quantity formula, state the major assumptions.
(b) State the objectives of codification. Discuss the essential features of a good codification system.
MS-4 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
Term-End Examination December, 2015
MS-4 : ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE FOR MANAGERS
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
Note : (i) Attempt any five questions.
(ii) All questions carry equal marks.
(iii) Use of calculators is allowed.
1. (a) Explain the 'Accrual Concept' and the 'Consistency Concept' in accounting and signify their importance to an accountant.
(b) Distinguish between 'Operating Profit' and 'Net Profit'. Which is a measure of operational efficiency of a company ? Distinguish between Capital expenditure and Revenue expenditure. Which is taken
into account for determining the Operating Profit ?
2. What do you understand by Fund Flow Statement ? How does it differ from a Cash Flow Statement ? Explain the main items which are shown in the fund flow statement and the purpose of preparing this statement.
3. What do you understand by Discounted Cash Flow Techniques of Capital Budgeting ? Briefly
explain the Net Present Value Method and Internal Rate of Return Method of appraisal of
projects. Which of the two would you rank better and why ?
4. Distinguish between :
(a) Profitability Index and Profitability Ratios.
(b) Earnings Yield and Dividend Yield.
(c) Fixed Budget and Flexible Budget.
(d) Direct Labour Rate Variance and Direct Labour Efficiency Variance.
5. Explain the following statements, giving reasons :
(a) Debt is a double-edged weapon.
(b) Depreciation acts as a Tax Shield.
(c) Fixed Costs are variable per unit and Variable Costs are fixed per unit.
(d) When the use of operating and financial leverages is considerable, small changes insales will produce wide fluctuations in Return on Equity and E.P.S.
6. "Zero-based Budgeting provides a solution for overcoming the limitations of a traditional
budget". Explain this statement and describe the process of preparing a Zero-based Budget.
7. Following is the abridged Balance Sheet of ABC Company Ltd. as on 31st March 2013.
With the help of additional information given below, you are required to prepare Profit and Loss
Account and a Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2014.
(a) The Company went in for re-organisation of capital structure with the share capital
remaining the same but other liabilities were as follows :
Share Capital 50%
Reserves 15%
5% Debentures 10%
Trade Creditors 25%
Debentures were issued on 1st April, interest being paid annually on 31st March.
(b) Land and Buildings remain unchanged. Additional Plant and Machinery has been purchased and a further depreciation (f 5000) written off.
(The total fixed assets then constructed 60%of the total gross fixed and current assets.)
(c) Working Capital Ratio was 8 : 5.
(d) Quick Assets Ratio was 1 : 1
(e) Debtors (4/5th of quick assets) to sales ratio revealed a credit period of 2 months. There
were no cash sales.
(f) Return on Net Worth was 10%.
(g) Gross Profit was @ 15% of sales.
(h) Stock Turnover was eight times for the year ignore taxation.
8. While finalising the plans for the Coming Year the excutives of XYZ Co. Ltd. thought that it will be advisable to have a look at the product-wise performance during the current year. The
following information is furnished :
MS-3 December, 2015
Written by sales@mbaonlinepapers.com sales@mbaonlinepapers.comMANAGEMENT PROGRAMME-
Term-End Examination
December, 2015
MS-3 : ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL
ENVIRONMENT
Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100
(Weightage 70%)
Note : There are two sections A and B. Attempt any three questions from section A, which carry 20 marks each. Section B is compulsory and carries 40 marks.
SECTION - A
1. What do you understand by Economic Environment in which a business firm operates ?Discuss.
2. Briefly analyse the growth and structure of Private Sector in India. Explain how does it contribute to economic development ?
3. Critically analyse the impact of regulatory framework on industrial structure and performance.
4. Differentiate between Current Account and Capital Account convertibility with reference to its role in rupee convertibility.
5. Write short notes on any four of the following :
(a) Economic Development
(b) Administered prices
(c) India's Foreign Trade
(d) Privatisation
(e) Development Banks.
SECTION - B
6. (a) What are the factors of widespread sickness among the Small Scale Industry (SSI)units ?
(b) How can sickness be identified ? Suggest measures to enhance economic viability of SSI.
7. How has the public sector in India been able to achieve the objectives of economic equity with growth ? Discuss with examples.
